Remote Docker
Remotely control your Docker engine
I was messing around with docker when I found out about something called as docker context. It is basically a way to control your docker instance which is on a remote server from your local machine. I thought that’s pretty cool.
And therefore, today we are going to explore it.
Diving in
Let’s look at the help options of it
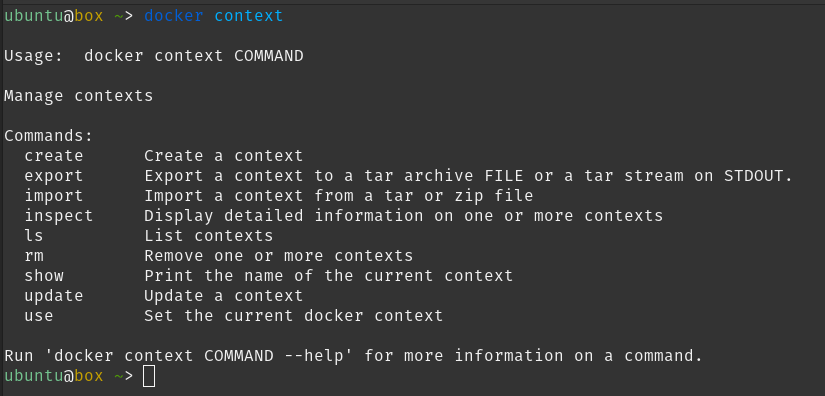
It’s pretty straightforward to use. We would be using create option to create a custom context.
Note: You need to have ssh key auth on your server to follow along. Otherwise, it won’t work.
So how do we create one? That’s simple too. We specify the host, ssh and description.
sudo docker context create --docker host=ssh://root@hostname --description 'test remote docker' myvm
Let’s break it down
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | We are using an SSH connection here. You could also use a TCP connection. Specify the appropriate hostname. |
| Description | Optional, but you could provide any suitable information about the context. |
| myvm | This will be the name of your context. |
After creating it, you can list it by using
docker context ls
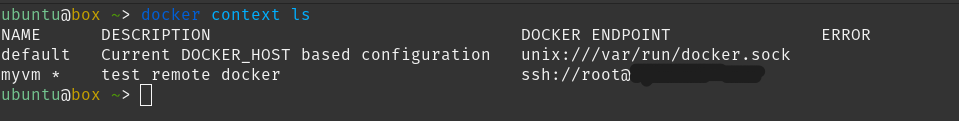
Now, comes the interesting part. Let’s use it by running the following
docker context use myvm
This will switch over to your custom context. Any kind of docker commands that you run will be executed on your remote machine!
If you want to switch back to the default context, run the following
docker context use default